R3 Practices by the Restaurants and Hotel Industry for Sustainable Waste Management in Pune
Corresponding author Email: gauristars@gmail.com
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CWE.16.3.21
Copy the following to cite this article:
Shah G. R3 Practices by the Restaurants and Hotel Industry for Sustainable Waste Management in Pune. Curr World Environ 2021;16(3). DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CWE.16.3.21
Copy the following to cite this URL:
Shah G. R3 Practices by the Restaurants and Hotel Industry for Sustainable Waste Management in Pune. Curr World Environ 2021;16(3). Available From: https://bit.ly/3lu2nfH
Download article (pdf) Citation Manager Publish History
Select type of program for download
| Endnote EndNote format (Mac & Win) | |
| Reference Manager Ris format (Win only) | |
| Procite Ris format (Win only) | |
| Medlars Format | |
| RefWorks Format RefWorks format (Mac & Win) | |
| BibTex Format BibTex format (Mac & Win) |
Article Publishing History
| Received: | 20-07-2021 |
|---|---|
| Accepted: | 06-09-2021 |
| Reviewed by: | 
 Sudheer Padikkal
Sudheer Padikkal
|
| Second Review by: |

 Rishikesh Singh
Rishikesh Singh
|
| Final Approval by: | Dr. Saravanan Pichiah |
Introduction
Each of us knows that plenty of food waste is generated at Restaurants, Dining halls, Catering facilities, Markets, the Food Processing Industry, and Households. However, 40% of the food purchased never gets eaten as per the statistics provided by the environmental research, which signifies the importance of waste management.11 India being a densely populated country and within India, Pune is one of the Major cities throwing out million metric tons of food every year, valued at crores; the issue makes the wasted food one of the most significant contributors to landfills producing harmful amounts of methane.
The research objectives are to understand the awareness and implementation of R3 practices in the Pune restaurants, the commercial benefits of R3 practices towards sustainable waste management, and the impact of R3 practices on Consumers as restoring effort for Environment.
The food is also wasted in buffet spreads and individual orders as well in the hotel industry. Research presented on Food waste management innovations in the foodservice industry on September 8, 2018, by Carlos Martin and Christine Meier concludes the growing importance of the reuse, reduce, and recycling processes. This paper represents various waste management initiatives undertaken in the foodservice industry, which vary depending on management's beliefs, experience, and aims. The concepts discussed in this paper help experts become more aware and encourage food waste innovations.
Furthermore, the research identifies that there is still a broader Scope to develop the refined process for sustainable waste management systems in every city. Pune restaurants make a sizable contribution to the total food wastage. According to the research done by the Chintan Environment group of Delhi, the wastage is more than actual usage. It is an ironic situation in a country like India fighting against Malnutrition for a long time. If the food gets donated before decaying to the needy people, it must term as reuse. Reducing food waste through surplus food redistribution by Paula Capodistrias shows the importance of food redistribution and how a company serves 3500 meals a day simply on food redistribution and supply of food. A similar practice is achieved by the various NGOs running in the Cities. Robin food, an NGO in Pune city, picks up the excellent quality leftover food from the destination and distributes it before getting spoiled. Direct surplus food redistribution in Norway is heavily dependent on the workforce of volunteers and personal relationships among the participating volunteers. This concept needs to be idealized in countries like India. There are many innovative ways to feed the hungry population while reducing food wastage. Must create awareness regarding waste management within the consumers and Hoteliers; much of the waste created in the hotels' industry from food- and beverage-department, vary in types like non-edible parts of vegetables, meat, or dairy, spoiled food, leftover good food, Expired Packaged Food, Refused food, and more. It is a priority that the actions need to be taken differently to each type of food waste to reduce the amount of wastage generated and improve the overall outcome of waste management processes. The research published on December 21, 2013, by Juha-Matti Katajajuuri focused on planning the volume and arrangement of avoidable food waste in the final food chain. It established that hundreds of million kg of food waste are generated each year from the household sector. The primary discarded food is usually fresh and perishable or leftovers from cooking and dining. The waste hierarchy consists of 5 R's: Reduce, reuse, recycle, recover, and residual management. However, this research is majorly focusing on the 3 R of waste management which is on top priority and doable to the Food Industry dealing with small-scale to large-scale businesses and various classes of employees with different backgrounds of knowledge and education. Civilized handful People know about the benefits of reducing, reuse, recycle and are Practicing them every day. While compiling the research data, the need for systematic, sustainable waste management is sensed deeply, improving the beneficial environmental contribution of the Food Industry of Pune and gaining commercial well-being. The consumers are very particular with the choices, and the portions in the modern world, which is a global opportunity to explore the endless possibilities and not only increase the footfall but also have massive savings up to 8% when it comes to costing by reducing serving portion sizes offering tasting facility and many more ways. Notably, the lead person in the industry is aware of the benefits of waste management practices. Mention of Food waste management,3R approach in selected family restaurants on May 1, 2013, By Mario Immanual, has an immediate effect on a nation's economy, including ecological results. A significant decrease in food waste might hold food costs from rising. For food selling businesses, protecting expenditure on extra food consumption or utilization commendably saves operational spending. This issue is fascinating to note genuine practices and understanding of food refuse. This real-time research endeavors to decide if there is any connection in the utilization of food Refuse towards the rules of Reduce. Similar research techniques can apply to the region of Pune where similar research lacks foolproof results. If the customers additionally get complete information relating to the techniques followed within the organization, their approach towards the company changes. The ground-level workers must undergo training to understand the importance of disposal practices. The research on Current and future trends in food waste valorization to produce chemicals, materials, and fuels: a global perspective is Published on June 2, 2014, by Egid B Mubofu, Carol Lin, and James Clark. This research majorly discusses all the techniques implemented by a restaurant for transformation and enzymatic reactions. A shift in food goes through chemical changes during the process of decay. The study of chemical changes is critical as it prevents them from happening in the unforeseen future. Food wastage created in necessary amounts is at present a nuisance around the world. While a large portion of these systems commonly offers a couple of employments not the same as landfilling or treating the soil, Modern valorization options ought to create to augment the worth from a, particularly significant waste source. This commitment shows various models and current valorization techniques proposed in multiple nations to handle food wastage. This research presents few methods to address food wastage, but it can relate to further research done in the region to understand the limitation and consequences the restaurants face due to following the proposed techniques, and then must submit modified plans after analyzing the research Gap Organizations require innovative measures to practice few R3 procedures, like giving discounts within the final bill, giving a special menu at discounted rate made of the stems, roots, seeds, or non-common components of ingredients, and lightening their nutritionary advantages to market them. Restaurants are also adapting with time, so are the people who want to try and taste different cuisines and cooking styles such as gasless kitchens and ancient cooking methods. An article published in the European Scientific Journal in June by Mona Choudhary, Jayveer Singh, Ravish Agarwal contributes to the research topic's knowledge with waste management initiatives in India for human well-being. The authors share the results that help the well-being of the human race in any region; hence, this research confirms that waste management using R3 in hotels holds a significant chunk of the perceived benefits. The aim of composing the study is to contemplate the current practices identified with the different waste administration organizations taken in India for human prosperity. another objective is to give a few ideas and proposals to develop further the waste Management followed in Indian cities. Existing reports identified with Garbage Disposal suggested by organizers/NGOs/experts/government bodies/Garbage generating industry Environment specialists/for further developing the framework. It offers information about the different waste management key factors in India and discovers the Scope for development in the same for the well-being of the society. This work is unique and could be additionally modified with the detailed research to the Food sectors only by developing individual systems of Increasing Awareness in consumers and professionals and training them to fulfill the requirements using limited available resources.
The Prominent Findings from Secondary Data with Eco-Friendly Techniques to be Followed
- Keep a list of favorite food and their required ingredients that is popular and customer favorites. It helps to buy the exact type of ingredient and, as a minimum, as required avoiding excess buying
- Avoid impulsive and unprepared buying, avoid buying of perishables if not sure of consumption
- Plan purchase list as per the storage and consumption capacity.
- Include quantities of utilizing to avoid overbuying - for example, salad greens - enough for a maximum 2-day sale.
- Prepare purchase list based on the material available in refrigerator or stores of the hotel and then maintain the par stock only for non-perishables
- Bulk purchases to save money can be made only for the needed quantities of perishable and non-perishable items.
The fact of relief is that many hoteliers are responding to the waste challenge. The awareness of the Hotel industry is increasing towards the sustainable mode of operation. Most luxury hotels have adopted the 'green' way of living to enhance customer satisfaction and pursue an eco-friendly lifestyle by making employees and guests aware of it. However, waste and Garbage disposal and management is a big issue for hoteliers.
Research Material and Method
Scope of the Study
This research has limited Scope of one city, which is one of the 1st tier cities of India and developing in all aspects very fast. There are also many potentials to explore this concept in Pune by many restaurateurs.
Sample Size
For Data Collection, a total sample of 50 owners and 80 consumers had randomly selected to attempt the customized questionnaire.
Sampling Techniques
The sampling techniques used were random sampling techniques for the Public/consumers and Stratified for the restaurant owners and hotel professionals from Pune city.
Data Collection
Primary Data was collected using a questionnaire.
Secondary Data was collected using the Literature available.
The customers, General Public which could be potential customers, and the restaurant's owners, fill a questionnaire survey. I have also gone to a restaurant to check if they follow Eco-friendly Practices and have had a short interview with them.
Analysis Techniques
Descriptive Analysis is used to explain the results obtained after conducting a survey. This research is qualitative, so the analysis is done on exploratory method, not by statistical method.
Results
R3 Awareness Among the Consumers
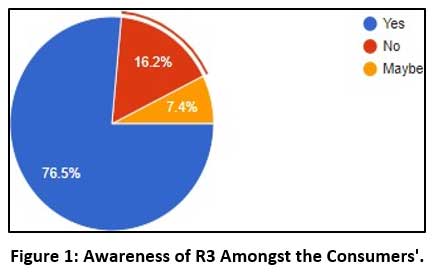 |
Figure 1: Awareness of R3 Amongst the Consumers'. Click here to view Figure |
The above pie chart shows that 76% of the sample population is aware of the R3 and its role in sustainable Waste Management, whereas 16% Population is entirely unaware of the R3 concepts. Also, 7.5% population is conscious of R3 but not aware of the implementation. The feedback confirms that the customers visiting the restaurants are aware of the R3 practices followed. They are also mindful of the environmental damage that happens when these efforts are missing. The Consumers are familiar because it is the independent subject of their interest, and the restaurant is announcing the R3 practices on all the social portals as a way of advertisement.
Declaration of Environmental Practices followed by the Food Industry is seen in the below Pie Chart
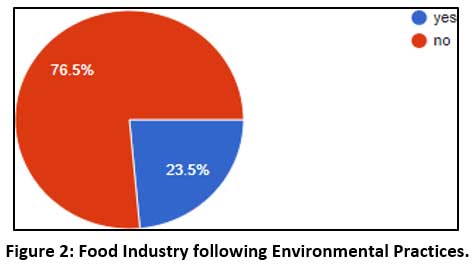 |
Figure 2: Food Industry following Environmental Practices. Click here to view Figure |
76% population does not take the initiative to understand the environmental practices followed by the restaurants or Hotels, only the 23.5% of the people whose keen interest is towards the well-being of the Environment or who are associated with the Waste Management due to various reasons take the initiative to enquire about Waste management procedures handled by the restaurants. It is now picking up like a trend, and especially a young age group wants to follow it.
Most effective followed Ecofriendly Practices by the Restaurants and Small Food Join can be Discussed with the Help of Chart below:
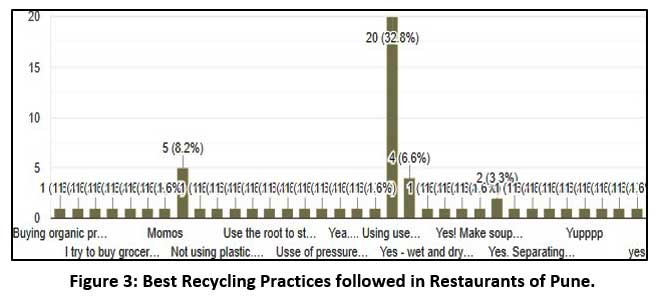 |
Figure 3: Best Recycling Practices followed in Restaurants of Pune. Click here to view Figure |
A few practices followed by restaurants daily are related to the convenience and efforts taken for these practices. following are the few methods that were in common for many sampling restaurants
- Reused oil – frying Oil can be filtered and used for tempering.
- Reuse of leftover food - Leftover preprepared sauces, only gravies or dips, can be used as marination or combinations to make a different baked or stewed product.
- Avoid plastic packaging by bulk buying. The recycling of packaging material is also possible.
- Collected refuse from raw Ingredients to make stock, chutneys, Preserves; sometimes these can be included as specialties by making innovative preparation (making green chutney of coriander stem and roots, making chutney of tomato, and fruit peels, using onion peels in making vegetarian brown stock).
- Compost of daily wet Garbage. -the spoiled or unusable leftover from the plate can be put in pits to make compost. This compost is suitable for in-house herb gardens.
- Taking pre-bookings to avoid excess unanticipated cooking. Pre-cooking and proper forecasting avoid excessive cooking, saving effort and food cost and eventually adding up to revenue.
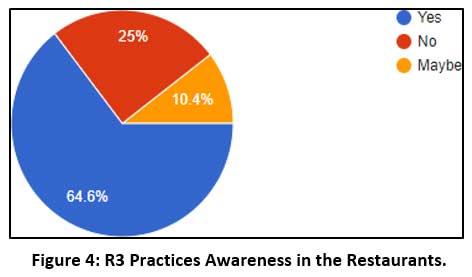 |
Figure 4: R3 Practices Awareness in the Restaurants. Click here to view Figure |
The feedback confirms that 63% of the restaurants' people were completely aware of the R3 practices followed in the organization.
The Measurable Impact of Implementing R3 Observed by the Organization which is shown in the below Pie Chart
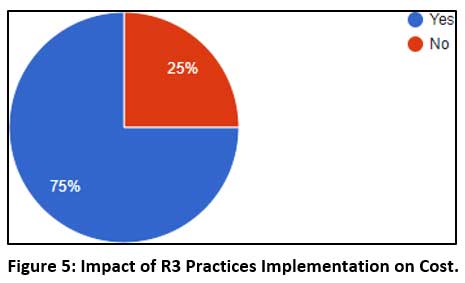 |
Figure 5: Impact of R3 Practices Implementation on Cost. Click here to view Figure |
75% of the organizers observed the impact of R3 implementation in the various costs and positive rise in controlling food cost which reflects in inevitable percentage hike of profit, all the expenditure towards the system changes of R3 needed to be considered as Asset cost to have it reflected in the savings and earnings.
Are you Identifying the Hurdles to Implement R3 Practices to support the Environment by the Organizations?
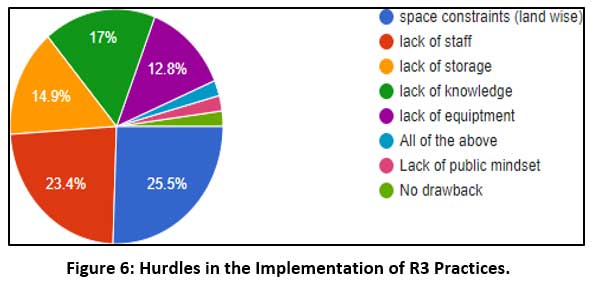 |
Figure 6: Hurdles in the Implementation of R3 Practices. Click here to view Figure |
Implementation of Environmental practices is a big task and involves logistic issues. For example, the research finds that many of the owners of Pune restaurants have environmentally beneficial intentions, but their staff and space do not allow them to implement the practices. Many a time, the team is not motivated enough to follow these R3 practices flawlessly.
Discussion
Most of the restaurants following this have seen a significant difference in cost-saving compared to the ones who haven't started with these practices, whereas the asset investment is sometimes more and running cost increases for a certain period till training of ground-level staff and knowledge building of the entire team does not happen.
- The feedback confirms that 63% of the restaurants' people were completely aware of the organization's R3 practices, and only a small percentage were not.
- The above chart shows that 45.6% of people are very likely to visit an eco-friendly restaurant whereas 30% are likely to visit eco-friendly restaurants, but 1.5% are not aware of the existence of any such restaurant, the remaining 23% of consumers would see the eco-friendly restaurant only once or sometimes for curiosity.
- Segregation of food based on the type and use- segregation is based on recyclable food, reusable food, and ultimately refused food—recyclable food to be given to the needy or poor. Reusable preprepared food can be stored well and used in other products without spoiling the quality. The part to focus on is that most people are trying to do their bit by conserving energy and reusing most of the leftover products at the end of the day. Unintentionally we conserve a majority of food production and try to reuse it in our daily lives. R3 practices followed in restaurants, also in houses, but the percentage needs to increase.
- Reuse, but don't compromise on quality and hygiene. Recycled cutlery and crockery are a good idea. Reduce wastage by maintaining proper portion sizes.
- Promote R3 to your customers. Try to educate people who get influenced to practice R3 regularly.
- Arth, one of the best contemporary Indian restaurants in Pune, followed an eco-friendly approach. They had a gasless kitchen, a firm believer of farm to fork, and curate daily menu depending on the raw material left with the kitchen back end. The concept of Arth makes them privileged as the consumer is curious every day and gets innovation every day. The survey shows that social media plays an essential role in eco-friendly marketing practices, so every restaurant should promote its business more on social media
- 76% of the population does not take the initiative to understand the environmental practices followed by the restaurant or Hotels, only the 23.5% population whose keen interest is towards the well-being of the Environment or who are associated with the Waste Management due to various reasons take the initiative to enquire about Waste management procedures handled by the restaurants.
- Segregation of food based on the type and use- Can segregate food based on recyclable food, reusable food, and ultimately refused food—recyclable food to be given to needy or poor. Reusable preprepared food can be stored well and used in other products without spoiling the quality. The part to focus on is that most people are trying to do their bit by conserving energy and reusing most of the leftover products at the end of the day. Unintentionally we conserve a majority of food production and try to reuse it in our daily lives. R3 is not only being followed in restaurants but also in houses.
- 42% of owners of environmentally friendly restaurants observe a reduction in food cost, which calculates up to 5% savings in the food cost. The reuse and remake policy can help to maintain food costs between 25 to 28%
Conclusion
The research had conducted to find restaurants and customers' perceptions, awareness about the eco-friendly practices followed in a restaurant of Pune, and the sustainability of these practices. Restaurants, with enormous scale, are adopting and implementing R3 practices in their daily routine to help with the production and saving of food costs and making a massive difference in their marketing and overall cost. R3 gives them many subsidies in the government and municipal taxation. The implementation of these R3 practices reflects in saving food cost, indirect popularity, and reach to the niche market of the environmentally-friendly crowd, being innovative in the menu makes the restaurant stand out differently. People nowadays are adapting to this concept because a lot of NGOs and activists are promoting the sustainable environment concept; personally, there is awareness within the individuals of Pune about R3 practices and their benefit to the Environment, but commercially there are plenty of hurdles to follow it in the food industry and keep it running for a long time. The concept of farm to fork is a part of this and had made a massive difference in how many of the brunches and menus to be curated around the locally grown produces and to stop the carbon footprints that increase if we use more foreign ingredients than local gowns. Many restaurants prefer to get their products directly from the farm and go to the source where their produce has come to ensure quality. Farm to fork is one of the indirect environmentally sustainable practices. This survey brings out the Scope where the city's restaurant owners can do their bit to help the Environment. This research also concludes the possibility of reuse raw preprepared food, recycling the food, food donation, and many more concept.
Acknowledgments
The researcher would like to acknowledge the restaurant owners and hotel managers to share valuable information; I would like to extend sincere appreciation to the reviewers who helped me make this article quality research.
Funding Source
The author received no financial support for this article's research, authorship, and publication.
Conflict of Interest
The author(s) declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Carlos Martin Rois, Christine Demen Meier, Stephan Gossling –"Food waste management innovations in the foodservice industry" on September 8, 2018. DOI: 10.1016/j.wasman.2018.07.033.
CrossRef - Francesca Girotto, Luca Alibardi, Raffaello Cossu. Food waste generation and industrial uses – A review, in June 2015. DOI: 10.1016/j.wasman.2015.06.008.
CrossRef - Mario Immanuel, Rafica Hartopo, Tommy Saroso, Samuel P D Anantadjaya Food waste management,3R approach in selected family restaurants, May 1, 2013, Journal of Management Studies, https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2280928.
- Michael A. Serio, Erik Kroo, Marek Wójtowicz, A Staged Pyrolysis and Combustion Process for Solid Waste Recycling in Fast Food Restaurants, December 21, 2007. DOI: 10.13140/2.1.2487.3760.
- Nazlina Yasin Mohd Hassan, Tabassum Mumtaz Mohd Ali Hassan, Nor'Aini Abd Rahman, Food waste and food processing waste for biohydrogen production- A review, September 2, 2013. DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.09.009.
CrossRef - Juha-Matti Katajajuuri, Kirsi Silvennoinen, Hanna Hartikainen Food waste in the Finnish food chain on December 21, 2013 DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.12.057.
CrossRef - Paula Capodistrias, Reducing food waste through direct surplus food redistribution -A Norwegian Case, May 2015. DOI:10.13140/RG.2.2.26803.53289.
- Mona Choudhary, Jayveer Singh, Ravish Agarwal, waste management initiatives in India for human well being in the European Scientific Journal, June https://home.iitk.ac.in/~anubha/H16.pdf.
- Egid B Mubofu, Carol Lin, Apostolis Koutinas, Avtar Matharu, Nikolaos Kopsahelis, James Clark. Current and future trends in food waste valorization to produce chemicals, materials, and fuels: a global perspective, Biofpr, June 2, 2014,https://doi.org/10.1002/bbb.1506.
CrossRef - Eng-Mohamed, EL-Sebay, wrote an article on Biomass from waste food, 2014, National Geography Magazine
- Joachim Venus, Daniel Pleissner, Green hotels published a research paper titled Use of food waste derived from hotels and restaurants to produce sustainable and biodegradable consumables, 2015. https://www.academia.edu/18546649/Green_hotels_-Use_of_food_waste_derived_from_hotels_and_restaurants_for_the_production_of_sustainable_and_biode
- Monika Choudhary, Sunanda Joshi, undefined Vartika, Lavisha Rao, Nidhi Srivastava, Bioprospecting of Enzymes in Industry, Healthcare and Sustainable Environment, 2021. DOI:10.1007/978-981-33-4195-1.
CrossRef - Gunders, Dana, How America is Losing Up to 40 Percent of Its Food from Farm to Fork to Landfill." Natural Resources Defense Council, 2017. https://www.nrdc.org/sites/default/files/wasted-2017-report.pdf.







