Water quality criteria and Arpa river water of Bilaspur city (C.G.)
Sudeshna Verma1 * and S.A. Khan2
1
Chemistry C.M.D. P/G College,
Bilaspur,
India
2
Principal Government Girls College,
Korba,
India
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CWE.2.2.16
The present paper aims to study quality of water in the Arpa river of Bilaspur district (C.G.). Standard testing method have been adopted for the measurement of water quality of Arpa river. Adoption of pollution abatement measures plays a great role in improving water quality.¹
Copy the following to cite this article:
Verma S, Khan S.A. Water quality criteria and Arpa river water of Bilaspur city (C.G.). Curr World Environ 2007;2(2):199-204 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CWE.2.2.16
Copy the following to cite this URL:
Verma S, Khan S.A. Water quality criteria and Arpa river water of Bilaspur city (C.G.). Curr World Environ 2007;2(2):199-204. Available from: http://www.cwejournal.org/?p=685
Download article (pdf)
Citation Manager
Publish History
Select type of program for download
| Endnote EndNote format (Mac & Win) | |
| Reference Manager Ris format (Win only) | |
| Procite Ris format (Win only) | |
| Medlars Format | |
| RefWorks Format RefWorks format (Mac & Win) | |
| BibTex Format BibTex format (Mac & Win) |
Article Publishing History
| Received: | 2007-06-05 |
|---|---|
| Accepted: | 2007-10-17 |
Introduction
Water quality is terms used to define the physical, chemical, biological of radiological characterstics by which a particular type of water may be establish its acceptability for various beneficial uses.2-4
Material and Methods
All the chemicals used were of AR grade. Double distilled water was used for preparation of reagents. Six strategic locations were chosen for the sampling of water. Those are Koni Petrol Pump (Station-I), Indira Setu (Station-II), Old Bridge (Station-III), Submersible bridge (Station-IV), Kanoi Paper Mill (Station-V) and Near Gatora Bridge (Station-VI). Water samples were collected in one-litre polythene bottles previously soaked with 8N.HNO3 and cleaned with detergent. The samples were acidified with 6N.HNO3 (8m/L) soon after sampling.
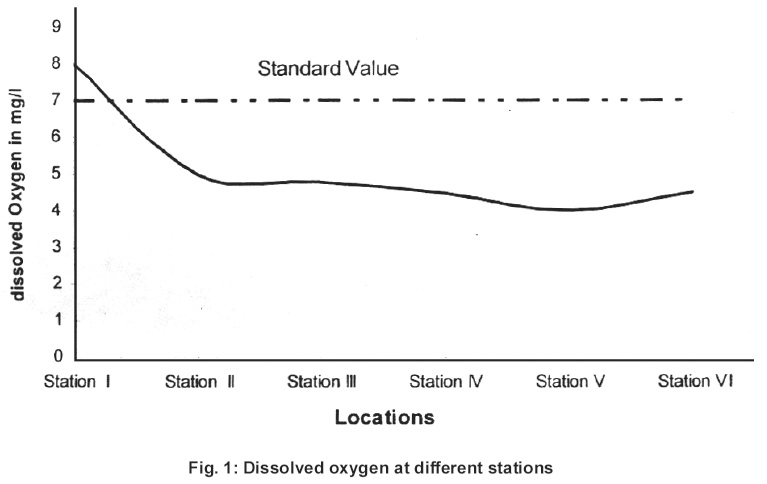 |
Figure 1: Dissolved oxygen at different stations. Click here to view figure |
Analytical Methods
PH of the sample was measured by pH meter (Orion pH meter model 940). Cd and Pb were determined (after complexiation and extraction) by AAS (Varion AA model 220). Conductivity of samples have been measured by Digital conductivity bridge (Systronics-304). The operation conditions for AAS have been described below in the Table 1.
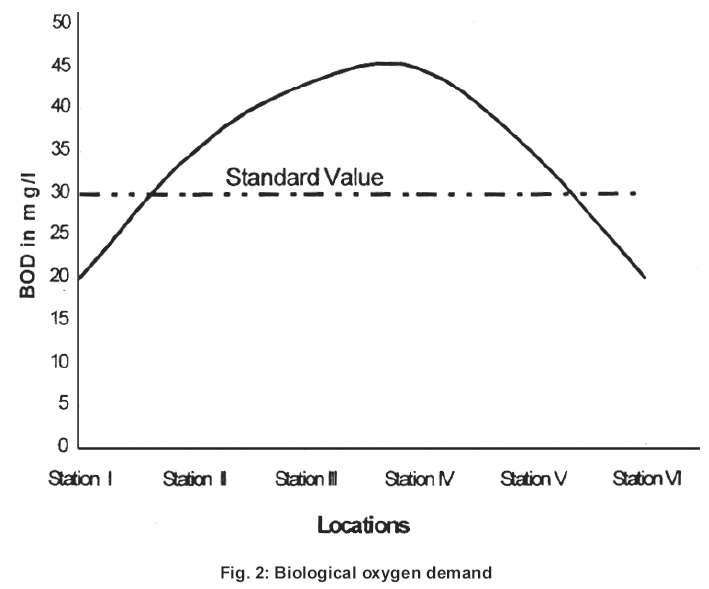 |
Figure 2: Biological oxygen demand Click here to view figure |
Dissolved oxygen (DO) and Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) were determined by prescribed lavoratory titrimetric methods.
Table 1:
| S.No. | Elements | Flame type | Slit | Lamp current | |
| 1 | Pb | 217nm | Air+C2H2 | 1.0nm | 5mA |
| 2 | Cd | 288.8nm | Air+C2+H2 | 0.5nm | 4mA |
Dissolved Oxygen (Wrinklers method)
300ml sample was taken in BOD bottle, then 2ml. MnSO4 and 1ml. Alkaline lodide Azide solutions was mixed with it 2ml. H2SO4 acid was added and titrated with 0.025N Hypo, using starch as indicator. The dissolved oxygen was then calculated using standard formual.5
[1ml of 025 N.Hypo solution = 1mg/l of dissolved oxygen]
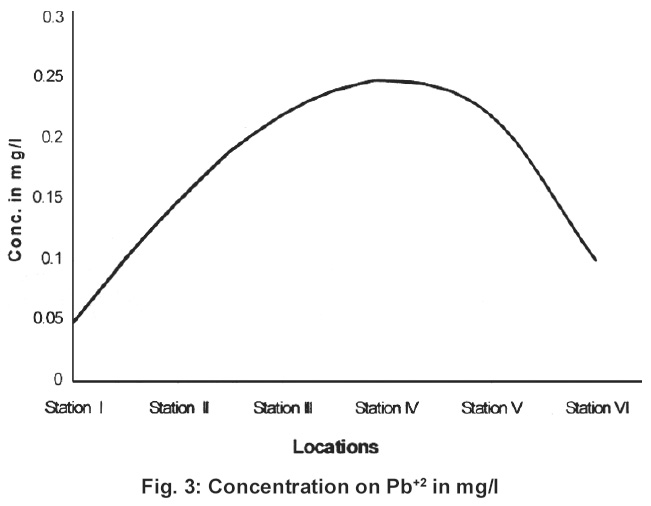 |
Figure 3: Concentration on Pb+2 in mg/l Click here to view figure |
Biological Oxygen Demand
Water sample were kept in the dark for five days. Then dissolved oxygen was determined using the Winklers titration method and calculated BOD using standard formula.5
Table 2: Indian Standards/Specification for drinking water is (10500.1083)
| S.No. | Paramaters | Limit | Unit |
| 1 | Colour Hazen units | 10Max | |
| 2 | Odour | Unobjectionatinable | |
| 3 | Taste | Agreeable | |
| 4 | Turbidity NTU. Max | 10 | |
| 5 | pH value | 6.5 to 8.5 | |
| 6 | Total Hardness (as CaCo) | 300 Max | mg/l |
| 7 | Calcium (as Ca) | 75 Max | mg/l |
| 8 | Magnesium (as Mg) | 30 Max | mg/l |
| 9 | Copper (as Cu) | 0.05 Max | mg/l |
| 10 | Iron (as Fe) | 0.3 Max | mg/l |
| 11 | Manganesium (as Mn) | 0.1 Max | mg/l |
| 12 | Chlorides (as Cl) | 250 Max | mg/l |
| 13 | Sulphate (as So4) | 150 Max | mg/l |
| 14 | Nitrate (as No3) | 45 Max | mg/l |
| 15 | Fluroide (as F) | 0.6-12 Max | mg/l |
| 16 | Phenolic compounds (as C2H) | 0.001 Max | mg/l |
| 17 | Mercury (as Hg) | 0.001 Max | mg/l |
| 18 | Cadmium (as Cd) | 0.01 Max | mg/l |
| 19 | Selenium (as Se) | 0.01 Max | mg/l |
| 20 | Arsenic (as As) | 0.05 Max | mg/l |
| 21 | Cyanide (as Cn) | 0.05 Max | mg/l |
| 22 | Lead (as Pb) | 0.1 Max | mg/l |
| 23 | Zinc (as Zn) | 5.0 Max | mg/l |
| 24 | Anionic Detergnets (as MBAS) | 0.02 Max | mg/l |
| 25 | Chromium (as Cr6+) | - Max | mg/l |
| 26 | Polynuclear Aromatic Hydrocarbons (as PAH) | - Max 0.1 | mg/l |
| 27 | Mineral Oil | Max | mg/l |
| 28 | Pesticides | Absents Max | mg/l |
| 29 | Residual Free Chlorine | 0.2 Max | mg/l |
| 30 | Radioactive material | ||
| a) Alpha emitters uc/ml | 10* | ||
| b) Beta emitters uc/ml | 10* |
Chemical oxygen demand
2Cr2O7 in 50% H2SO4 at a reflux temperature. Ag2 SO4 was used as a catalyst. The excess of K2Cr2O7 was titrated with standard Fe11 (NH4)2(SO4)2(hypo) using ferrion as an indicator. Principle reaction is

Results and Discussion
Organic substances in the samples were oxidized by K
 |
Figure 4: Concentration of Cd+2 in ppm Click here to view figure |
These figures inform about dramatic change in water quality parameters. Hence the Arpa river water is rendered unsuitable for drinking in the city area. The Arpa river is shallow but life line of Bilaspur city. Increasing population and rapid industrialization in the last few decades have icreased pollution in the potable river water. Dissolved oxygen decreases from point no 1 to 4. Paper mill at point, throws chemicals containing alkali and plant degradation products.
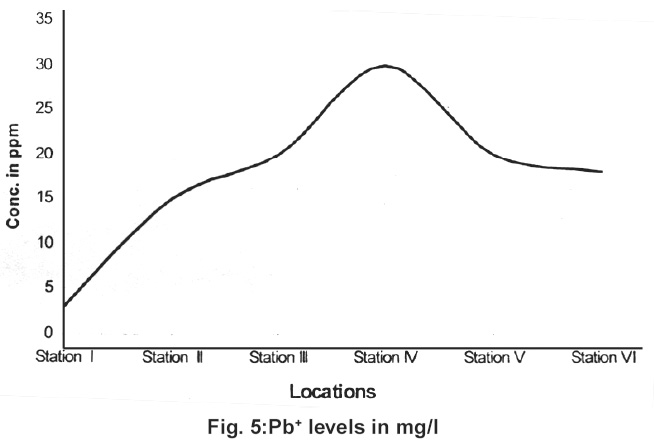 |
Figure 5:Pb+ levels in mg/l Click here to view figure |
In the present study temperature ranged form 25°C to 29.5°C. The pH value ranged from 6.9 (Location) 8.69 (location 5) of the Arpa river. Location 5 and 6 show higher values than the prescribed limit.6
Total dissolved solids (TDS) ranged form 230mg/l station to 1500 mg/l (station 4,5,6,).
Table 3: Classification of water quality.10
| S.No | Paramter | Good |
Clasification Fair |
Poor |
| 1. | Temperature | 25 | 27 | 30 |
| 2. | pH | 6.5-8.5 | 6.5-3.5 | 6.0-9.0 |
| 3. |
Electrical conductivity |
3.25 × 10 mhos/cm | 3.5 × 10 mhos/cm | 4 × 10 mhos/cm |
| 4. | Dissolved O2 | 7 mg/l | 6 mg/l | 5.5 mg/l |
| 5. | Pb in mg/l | 0.01 mg/l | 0.01 mg/l | 0.05 mg/l |
| 6. | Cd in mg/l | 0.003 mg/l | 0.004 mg/l | 0.005 mg/l |
According to and Indian standards as shown in the Table 3, TDS should be less than 500mg/l for drinking water Table 3. The dissolved oxygen between 4 to 8 mg/l. The standard limits is 7mg// for drinking water.8 The BOD ranged from 20mg/l to 45mg/l. The standard limit is 30mg/l.9 Chemical oxygen demand (COD) was determined by titrimetric method. COD value informs about organic matter present in the drinking water.
Depletion of dissolved oxygen in water supplies can encourage microbial reduction of NO3-1 to NO2-1 and SO4-2 to S-2 giving rise to odour problem. The Electrial conductivity value ranged between 0.50 to 6.15 × 10-3 mhos/cm to 6.15 × 10-3 mhos/cm in the present work. Higher values area 3.30,4 5.2 × 10-3 mhos/cm at locations 2,3,4,5 and 6 and water is unfit for drinking.
Standard values Pb and Cd concentration s for potable water are 0.1 mg/l and 0.003 mg/l. In the present work higher values have been found in the stations 2,3,4,5 and 6. Classification of water quality has been described in the Table 3. below.
Conclusion
Rapid urbanization and increased anthropogenic activities have deteriorated the water quality parameter of Arpa river water. Therefore the pretreatment is essential before supplying for drinking purpose. (This also applies to ground water). Following methods have been suggested as remedial measures.
Remedial Measures
- Flyash, a waste product from coal combustion can be employed as a low cost adsorbent for the 11 treatment of Arpa river water. Kapadia et al have reported that fly ash removes metals lowers oxygen demand. Some authors have also suggested that it removes colouring material from waste water.12
- We propose treatment of Arpa water by photocatalytic degradation of BOD, COD, iron and E-coli bacteria. The solar detoxification is the process in which catalyst, for example TiO2 is exposed to the sun. The catalyst absorbs high energy photons from UV. Portin of the solar spectrum and reactive free radicals (OH) are formed. These free radicals are powerful oxidizer and disinfectant. In general a concentration of 0.1% to TiO2 is quite, effective in killing bacteria. This is quite in agreement with works is Kaushik. N.D. et al.14
- Vermiculite, a type of mica adsorbs fluoride ion.15 Hence this can be used for treatment of water to remove fluoride ion.
These abatement measures play a great role in improving water quality of Arpa river water.
References
-
F. Coulson and Mark E., Proceeding of an international Forum. America Sanfranciso (1977) pp 51-56.
-
Hooda. S. and Kaur, S. Laboratory manual for environmental chemistry. S. Chand and Co. 1999 ed (1991) pp 18-52.
-
CPCB. Pollution Control Acts, Rules and Notifications issue there under spet. (2001).
-
Hasan, M..Z. and Pande, S.P. Estimation of Cd and Pb. Ind. J. Envi. Hlth. (1978) 20: 232-24.
-
Allegria A., Barbera R., Boluda R., Errecalde., F. et al. Environmental Cd, Pb and Ni and its possible relation between soil and vegetable content. Fresenius. J. Anal Chem. Springer Verlag. (1991).
-
Kabata-Pendias A., Pendias, H., Trace elements in plants and soils. CRC Press. Inc. Boca Raton. Florida (1984).
-
Yoshikawa. H. et al. Indian Health Ed. (1974) 12: 127-140.
-
Foulkes, E.C. Absorption of Cd in: Hand book of Experimental Pharmacology., 75-100. Berlin New York. (1986).
-
Environmental Science Series: Environmental Pollution of Cd, Bio, Physiological and Health effect. By Nath. R. Published by mehta House, New Delhi (1990).
-
Jones. M., David O., Johnsten J.T. et al., Chemistry and Society, Saunders College Publication. New York pp 405 (1987).






