Study on Challenges of Disaster Management in Urban Heterogeneous Tissues (A Case Study in Hassan Abad Spot)
Molaee Rahil1 and Baghdadi Arash2 *
1
Department of Urban Planning,
ShahreQods Science and Research Branch,
Islamic Azad University,
Tehran,
Iran
2
Department of Urban Planning,
ShahreQods Branch,
Islamic Azad University,
Tehran,
Iran
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CWE.9.2.17
This article discusses strategies forcrisis management in metropolitan heterogeneous areas. Hetero geneous urban bounds are worn areas in addition to facing people with physical, social -cultural and economic problems, they have been developed with in oradjacent urban tissues. The juxt a position of hetero geneoust issue deterioration, particularly in crisisen counter sadjacentareas to face serious threats.In this study situation of economic, social, cultural, migration, hetero geneous structure of Tehran city are examined.Methodology of this was an analytical approach that different prospects of urban planning view and crisis management solutions have been described.
Copy the following to cite this article:
Rahil M, Arash B. Study on Challenges of Disaster Management in Urban Heterogeneous Tissues (A Case Study in Hassan Abad spot). Curr World Environ 2014;9 (2) DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CWE.9.2.17
Copy the following to cite this URL:
Rahil M, Arash B. Study on Challenges of Disaster Management in Urban Heterogeneous Tissues (A Case Study in Hassan Abad spot). Curr World Environ 2014;9(2). Available from: http://www.cwejournal.org/?p=6518
Download article (pdf) Citation Manager Publish History
Select type of program for download
| Endnote EndNote format (Mac & Win) | |
| Reference Manager Ris format (Win only) | |
| Procite Ris format (Win only) | |
| Medlars Format | |
| RefWorks Format RefWorks format (Mac & Win) | |
| BibTex Format BibTex format (Mac & Win) |
Article Publishing History
| Received: | 2014-02-11 |
|---|---|
| Accepted: | 2014-05-17 |
Introduction
Mankind from the beginning until now has been grappling with a variety of natural events and have grown between threat sand often irreversible damage have entered because of crisis caused by the invasions on human society. In all countries,especially developing countries, the in creasing pace of urbanization continues and it is as a threat to the irhigh damage in the even to fnatural disasters or invasions.Uncontrolled growth of urban population without coordination with the development of infrastructure in urban areas,environmental pollution and poor quality of life,burn out texture has made most of regions to have uncontrolled margins and heterogeneous spots in the issue of metro politans such Tehran city. Due to in attention and neglect of urban primary core and old city, and adding the core radius without strengthening the centers, and today metropolises like Tehran encountered critical problems and crises.
Presence of social, economic, physical heterogeneity in some areas of the city, provided abnormalities. These anomalies that are called urban uneven spots, have lots of problems and these cases in crisis, made the problems more than usual situations.
In quiet community situation, presence of such old neighborhood beside the new neighborhood, not only in make Tehran spiky, so threatening and devastating. Imagining the uneasy atmosphere for the community in times of war, earthquakes and other natural disasters there will be unforeseen circumstances. Degradation with in the context with greater intensity (relative to the relaxed state), and heightened insecurity and as a consequent inability to deal with the crises are of issues that anysocio-economic and political organization should remedy for them according to their own needs.
These problems in big cities, especially Tehran that strategically has also a unique position in Middle East is so important. So the main aims of this paper are to examine the challenges of crisis management in such areas. Accordingly, the specific objectives of the research are:
- Study of structure and texture of the region(state of roads/street mode/height of buildings/population density)
- Study of social status of the area
- Study of economic situation in the region
- Study of crisis management functions in these areas
Study Area
In the northern parts of Tehran, in addition to tissue aging of the initial core focus that were rural focuses and declining the standards, encounter with acute problems including facing the new neighborhood along with old neighborhood. The primary cores and old dense of northern Tehran, were residence area of indigenous residence area people, and some immigrants from other parts of the country that nearly were homogenous and with increasing immigration growth, not repairing, and also because of low price of housing have changed to slums into the adjacent neighborhoods and immigrant populations with low -absorbing economic and overflowing of crowding from desirable neighborhoods (Baghdadi, 2007).
Presence of developed areas with probably about 50 meters away from old cores has created problems in this area. A number of old residents who numbers are not less with indigestion gap affluent neighborhood residents against new positions and social and cultural conflict and conflict have exacerbated the problems of poverty and economic and cultural development and the conception of crime and victimization, and ultimately creates criminal closes and untenable spaces (Baghdadi, 2007).
These areas develop into undesirable categories of criminals and create an unsafe environment for residents that probably any error happens in it and have been shown that social quiet conditions are of threat and very destructive.
Residential unit sin this area are very small,with poor construction, poor design and poor technical infrastructure and non- resistance and mostly are made of non-standard units. New housing units have been formed in the initial fragmentation into smaller units.
Networks are non-normative, non-standard, inefficient and dangerous. The lack of urban planning in these are as has led to creating a narrow passage way that welcomes any danger to its residents in times of crisis(Baghdadi, 2007).
Literature
If we define, management as a science and art of coordination, leadership and control of social activities, to reach to favorite goals with the highest performance, crises management can be defined as: a natural or man-made disaster that creates suddenly or increasingly and imposes hardship to human societies in a way that in order to eliminates it, the need for extra measures are essential (Memarzadeh and Sarfarazi, 2010). In fact, risk management refers to the set of actions that occurred before, during, and after the accident, to minimize side effects (Ghanavati et al, 2009).
Kind of threats and dangers
Since the beginning of mankind, human have grown among threats and in order to resist against of them have thought about different measures, some of threats are not existed, the severity of some threats are more or less and some of them are new and novel.
In recent decades, the way to deal with these threats have taken a more scientific and in particular the amount of damage, and how to deal with them have been determined(Asgharian Jadi, 1386).
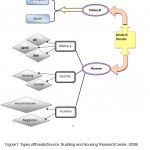
Threat are classified in to two categories including natural and man-made. Natural threats like floods, earthquakes,hurricanes and man-made threats are classified in to three categories:
- Military threats
- Security threats
- The threat of accidental
Threat of military invasion consists of air, land and sea. Security threats, includes sabotage, bombings, and so on and accidental threats are fires, explosions or spills, fuel tanks or leaking of hazardous materials (Center of Housing and Building Research, 2009).
|
|
Figure 1: Types of threats (Source: Building |
From the areas, that particularly in the case of a disasters such as the earthquake and war damage is incurred, are urban areas that makes clear the necessity of crisis management. An example of the errors that occur simply in crisis management is that suppose to be one solution for all crises, while because crises are caused by a variety of sources, a number of factors play a role in their occurring. So, for controlling them, different projects and ways should be implemented (Qavacati et al, 2009).
In "urban areas" of common deleterious effects caused by natural disasters or threat so f aggression including physical damage and dysfunction of the consolidated city. Demolition of residential structures, networks and access roads, urban infrastructure, such as telephone, electricity, water piping, etc. are included.
Injury rates in cities in crisis situations is highly dependent on its structure, so, the death rate that is of another dimension of the crisis, especially in areas that have large populations or compressed tissue is, it will be greater (Safari el al, 2010).
The role of topography and land Steep are direct factors in the impact of threats, and increase in the rates of damage or casualties. In other words, the location of buildings when they are built on a slope or when the materials are made of heavy contributes increase the mortality rate.
If crisis management has broader concept of reconstruction after the accident and taken in the short term or long term in that sense, a broader communications planning and urban design and architectural finds will be created (Yeganegi and Bayat, 2011).
Structure and texture of Hassan Abad region
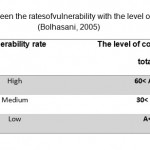
Each of tissue of city based different indexed including regular and irregular, dense and sparse, fine and coarse, and full and empty spaces are reviewed.In fact the context of a city is its shape, size, and how the smallest combinations of components are that will be effective against the military and civil disasters (Bolhasani, 2005). Distribution of elements space, composition and functions of the city's main role have important role in vulnerability of the city in various events, particularly in aggressive attacks.
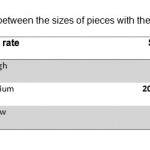
Textures of heterogeneous areas are presented in dense,irregular and small pieces with irregularities in fill and empty spaces and have very limited degree. In the se neighborhoods, many narrow ways and twisting restrictions are seen and in narrow alleys as far less than 3 meters in width and 30 percent steep, building of residential buildings with a height of 5-stories are seen.
Most of heterogeneous net work traffic in the area have been created mostly with out previous designs and has an irregular structure and accesses are often walking sides.
Dead end of texture,are with less than 6 meters in width and the permeability coefficient of them are less than 30% and this type of structure in the case of risks, make very hard situations, for aid operations.
High steep, out door pieces and curbs and placement of buildings will make the security,privacy of the residential units in endangered situations. However, grained texture prepare the escape and refuge conditions for criminals but because it provides a completely open space and safe conditions for escape and refuge, so aid operations to residents in the case of risks and natural disasters relief will be very hard will lead to high mortality.
|
|
Figure 2: Fereiduni dead end in Omrani street |
Another problem with the approach of passive defense is made of the out door area, which is higher than the standard range when the crisis fails.
|
|
Table 1: Relation between the rates of vulnerability |
|
|
Table 2: Relationship between the sizes |
The high density of buildings and population in these areas, prepares a situation exacerbated by injuries and damages, and seek to impose higher costs than other urban areas. High density of buildings and population in these areas, are dense and compressed that lead to high vulnerability in times of crisis and will incur additional costs.
The social status of Hassan Abad,Tehran
The textures of these areas are combination of simple or relatively skilled industrial workers or drivers who often have relatively low income and a social layer that is completely parasitic, or ethnic or folk origin or are composed of different immigrants that because of dark activity, violent criminal and corruption are at very low levels (Baghdadi, 2007).
Immigrant residents in these heterogeneous regions often have come to Tehran due to lack of adequate economic and cultural facilities of villages or cities and in many cases create non expert jobs including oil changes or retail.
Corrupt activities in this area for many residents, especially among young people and adolescents who are often indifferent to education, are very common and most of these persons are addicted.
Immigrant population and low economic power persons, overflow crowd that are away of more exhaustive than desirable neighborhoods have been forced to choose to live in the old neighborhood because of low housing prices. In fact, such unsafe environments for the residents are safe place for encouraging criminals.
|
|
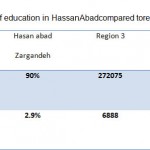
Table 3: Level of education in Hassan |
|
|
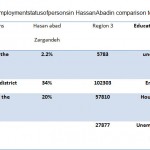
Table 4: Employment status of persons |
|
|
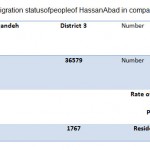
Table 5: The immigration status of people |
Study on function of disaster Management in Hassan Abad, Tehran
Crisis management due to the increasing power of inhibition, have important role in initiating to reduce risks of military conflicts or natural disasters and can reduce the devastation caused by the invasions or natural disasters to some extent.
Crisis management can be used to establish crisis management activities necessary to ensure a secure communication network and the communication system established in the cluttered situations.It also provides support requirements and satisfies of all the essential requirements of safes paces in times of crisis, and the distressed neutral event before and after accidents (Safari et al, 2010). Assess the extent of damage and injuries in one of the most efficient levels directly use in spatial planning and urban ism.
In heterogeneous urban spots, influx of rural migrants, overpopulation, improper positioning, pieces of fine and dense textures, texture instability, poor design and non-resistance of technical and organic impenetrable network, unprincipled, and the urban poor structure and such characteristics have important role in increasing amount of damage to cities. So, what makes the threats of natural and man-made disasters, to cities with turning to a range of disabilities, in many cases are due to the poor condition of the cities. This situation can be reduced by correcting situations of cities, vulnerability of towns in facing to crises to high levels and can be establish cities resistance to disaster.
|
|
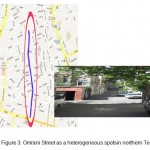
Figure 3: Om rani Street as a heterogeneous |
Result
Proximity of diverse heterogeneous areas to developed areas of the cities, make particular view in the time of crisis. Areas such this, that aid operations and reducing of dangers and death are nearly impossible, and with positioning of them in close to another regions, dangers and threats for another close areas will intensify. Probability of people, who are living in non-transparent way, will be a risk factor in times of crisis. High overflow of population, leaving the heterogeneous zone, which inevitably have to go through the neighborhoods adjacent to the highway networks and reach the main streets, lead to the lack of authentication services to the residents of the surrounding safe areas.
Regarding to these incorrect social behavior and the problems can create during times of crises by residents of old neighborhoods to high employment levels residence and regarding to fine texture and high level of occupation it can be concluded that heterogeneous areas in times of crises can be problematic. So,they need more attention than other metropolitan areas.
Regarding the ranges of heterogeneous areas in the city and their needs, specially in crises conditions, in addition to identification of heterogeneous areas in metropolises and to prevent of their creating, following solutions will be presented in order to reduce damages to them in threats and crises situations
Systems capable of planning for heterogeneous areas in the times of natural disasters or invasions, is municipal which due to the nature of these areas,have a main role in reducing the damaging effects of invasion, or natural disasters have (Baghdadi, 2007).
Among the actions that can be done in these areas, reconstruction of neighborhoods and integration of body, texture, quality of heterogeneous structure with texture and structure of adjacent neighborhoods. It also has social and cultural homogeneity and the best and most appropriate way of reducing risks and vulnerability at times of crisis.
Other measures are including integration and over all injured and destroyed tissue, but the problem is also possible and it is a little hard to be done.
Such activities relate on city officials and if doing in proper and principle manner, can guarantee security against threats and aggression management to control the crisis or natural disasters.
Other measures in the short-or long-term will be as follows
- Identify the uneven spots and threat assessment (attack or natural disaster) in these areas
- prioritize critical facilities in each of these areas in times of crisis to mitigate threats
- Develop plans on how to deal with the crisis of the urban centers
- Develop a list of the most vulnerable areas in the context of the threats and their classification
- Identify risks in times of crisis
- Use of community participation in neighborhood and class preparation and learning to deal with crises
- Planning, managing at the macro level in all areas, including social, cultural and economic in the country and crisis management and monitoring programs in the entire country.
- Research on legislation needed to facilitate the implementation of mitigation and crisis management plan for review and approval in accordance with the priority set based on rules
- The decentralization of Tehran.
- Funding allocation and risk management, especially for the promotion of Tehran as a metropolis of the Islamic World
- Reducing the growth rate of city community in a way that shows risks and try to prevent immigration to Tehran that is under threats and natural disasters.
|
|
Figure: 4 |
Conclusions
Rapid growth of urbanization and immigration that has not been planned, creating non-principal organict issue as well, will increase the like lihood of casual ties and damage occurring because of natural disasters, or in the time of the invasions and crisis.
In these situations, the things that lead to losses and break the unity of the city in crisis times, are fragmented parts of the city. Each piece is based on class, race, culture and religion and does not seem to be a unique during the crisis. Each group thinks about its needs even with putting its adjacent neighborhoods in danger.
Top level neighborhoods in close to low level socio-economic regions, are very dangerous and prepare special situations for opportunistic persons in heterogeneous areas.
With performance of operations that have been designed in short-term and long-term measures for the implementation of the proposed solutions, we will have cities with safer neighborhoods and less vulnerable in order to minimize injuries and damages to urban crises that is an important step to be taken.
References
- Baghdadi, Arash. (2007) "An analytical approach to the uneven spots in the context of Tehran". Hoviyate shahr Journal, First issue, No. 1, 62-51.
- Building and Housing research center (2009) Draft of twenty-first issue on National Building Regulations.
- Memarzade, Golam Reza; Sarfarazi, Mehrzad (2010) "Investigation of growing steps in crisis management organization" Department of Social and Cultural Studies - Page 13
- Baghdadi, Arash. (2010) "Identifying the scope of municipal assets and present its position in terms of passive defense" Maleke Ashtar University, Tehran.
- Poormousavi, Sayed Musa, Firoozpoor Armin and Darani, Masoud (2012) "The role of the community in the improvement of Crisis Management Systems," Journal of Disaster Prevention and Management, Volume II, Number One,42-32.
- Hamidi, Malihe (2005) "The role of planning and urban design mitigation and crisis management," Proceedings of the International Conference on Seismology and Earthquake Engineering, Volume 2,1660-1654.
- Sarbaz, Najmeh. (2009) "Urban heterogeneous coordinate constructions" Culture and Society Journal, Volume 1, Issue 27.
- sharifinia, Zahra. (2012) "marginalization and social and cultural issues in the cities," Fourth Conference on Planning and Urban Management.
- Safari, Abbas; Shokoohi, Ali; Aslanian, Yashar (2010) "The effects of urban planning and crisis management in reducing earthquake damage.
- Fathi Rashid, Ali; Qolizadeh, Elham (2006) "The urban worn passive defense". Tehran Safe Community Conference Proceedings, 48-33.
- Qanavati, Ezatollah; Ghalami, Shabnam;Abdoli, Asghar. (2009) "Empowering the Urban Crisis management in order to reduce the earthquake disaster," Journal of Geography, first issue, (4), 15-23.