How robust is executive summary in an environmental impact assessment report for decision-making: an Indian case-study
1
CEPT University,
Gandhinagar,
Gujarat
India
Corresponding author Email: drakarathi@gmail.com
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CWE.13.Special-Issue1.02
Copy the following to cite this article:
Krishan G, Chandniha S. K, Lohani A. K, Yadav B. K, Arora N. K, Singh S, Kumar C. P, Sharma L. M, Bhardwaj A. K. Assessment of heavy metals in relation to soilpollution atMewat, Haryana, India. Curr World Environ 2018;13(Special-issue 3-2018). DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CWE.13.Special-Issue1.02
Copy the following to cite this URL:
Krishan G, Chandniha S. K, Lohani A. K, Yadav B. K, Arora N. K, Singh S, Kumar C. P, Sharma L. M, Bhardwaj A. K. Assessment of heavy metals in relation to soilpollution atMewat, Haryana, India. Curr World Environ 2018;13(Special-issue 3-2018). Available from: https://bit.ly/2ADfaVj
Download article (pdf) Citation Manager Publish History
Select type of program for download
| Endnote EndNote format (Mac & Win) | |
| Reference Manager Ris format (Win only) | |
| Procite Ris format (Win only) | |
| Medlars Format | |
| RefWorks Format RefWorks format (Mac & Win) | |
| BibTex Format BibTex format (Mac & Win) |
Article Publishing History
| Received: | 2018-09-29 |
|---|---|
| Accepted: | 2018-10-27 |
| Reviewed by: | 
 Ayona Jayadev
Ayona Jayadev
|
| Second Review by: |

 Polash Banerjee
Polash Banerjee
|
| Final Approval by: | Dr. Satish Wate |
Introduction
Executive summary of a report is defined,1 as a “brief but comprehensive synopsis of a business plan or an investment proposal, which highlights its key points and is generally adapted for the external audience”. An executive summary,2 or “management summary is a short document or section of a document, produced for business purposes, that summarizes a longer report in such a way that the readers can rapidly become acquainted with the large body of material without having to read it all. It usually contains a brief statement of the proposal covered in the main document, background information, concise analysis and main conclusions”. Executive summaryis construed asan extremely important component of any business plan and is meant to facilitate a manager in making decision on the proposed plan. Unlike ‘abstract’, “extensively used in academic research,which is a brief summarizing statement read by parties who are trying to decide whether or not to read the main document, ‘an executive summary’ is a document in miniature,2 that may be read in place of the longer document”.An executive summary is customarily the first portion of a project report or business plan, and is intended to summarize its entire content, whilehighlighting the crucial aspects. In addition to giving introduction to the report, executive summary should be able to serve as astandalone documentgiving an overall outline,3 of the report.Considering that the reader will onlyread executive summary part of the report, and then decide whether to read the detailed report, it is extremely important to include an outstandingsummarization,4 of the report.
Executive summary,5 is a “concise discussion of significant findings and recommended actions”.It highlights the key findings,6 of the environmental impact assessment (EIA) for the proposed project to meet with the EIA regulatorystipulations. The key aspect of the executive summary is that it clearly brings out the action pointswhich are needed forimplementation.7 In addition to describing the essential features of the project, the executive summary needs to include.8 the objective of the report, the major potential impacts and the action plan proposedfor addressing these impacts.The EIA regulation.9 in India prescribes that summary of the EIA report, condensed to ten A-4 size pages with project description, description of the environment, anticipated environmental impacts and mitigation measures, environmental monitoring program, additional studies, project benefits, and environmental management plan be preparedandtranslated in the regional language, and made available in public domain for public consultation.
The major focus of EIA researchers and professionals has been on the key areas of EIA like environmental impact assessment, consideration of alternatives, and EIA follow-up. Executive summary part of an EIA report, which is the only part often read by most of the stakeholders including decision making authorities in place of the main report, has received little attention in the literature. With this consideration, the present study, possibly the first of its kind, was undertaken to evaluate the robustness of executive summary in EIA reports prepared in India, and to propose guidelines for the preparation of executive summary.
Guidelines for Preparation of Executive Summary in EIA Reports
An executive summary “must describe each significant environmental issue and its resolution in sufficient detail so that the reader can understand its importance and scope, as well as the appropriateness of the approach10 taken to resolve it along with a clear presentation of the critical facts that make up each issue”. The presentation needs to be made more effective with the help of base maps, tables, charts and figuresas far as possible. The information should be compressed into compact, but purposeful presentations. The executive summary gives a synoptic description of the main findings and recommendations with a focus on the essentialfacts and alternatives for decision-making, and is not meant to encapsulate allthe contents11 of the EIA report. Sinceonly the executive summaryportion of the report is usually read by decision makers and other stakeholders, it should be kept short, preferably lessthan seven pages11 except for very large projects where it could be little longer. Considering that EIA is used in the decision making process, non-technical summary,12 without including specialized language or complicated figures, should be accessible to the public in such a way that it is understood by the informed lay-person13. “Executive summary should be accessible and understandable14 to members of the interested and/ or affected community”. It should be written in a simple language with an overview of the project, the alternatives considered, the time schedule for construction, the potential environmental impacts, proposed mitigation measures, environmental monitoring, and environmental management program15 (EMPg). It should conclude by pointing out the residual impacts of the project after the suggested mitigation measures,followed by an overall conclusion on the environmental viability16 of the project.
The EIA team leader15 prepares the draft EIA report by compiling and collating the reports received from different functional professionalswhile ensuring uniformity, consistency, completeness, smooth flow of the language, and logical sequencing of the contents in each chapter of the EIA report. Thereafter executive summary is prepared, strictly based on the material in the draft EIA report, and is generally placed before the first chapter of the EIA report. The EIA review mechanism15,17in India consists of review of EIA reports by expert appraisal committees at central and state levels having part-time nominated members with different background and expertize, often not directly related to EIA. These committees get a large number of project proposals for seeking environmental approvals. The committee members are under severe pressure of time and may not be able to review each EIA report thoroughly. As a result, most often, they are likely to be forming opinion on the information contained in the main body of the EIA report based on the executive summary only. Other stakeholders may also be reading this part of the EIA report only. At the same time, considering that a lot of resources18 go into the preparation of an EIA report, it is necessary that executive summary describes complex contents concisely, simply and accurately11 in a non-technical manner for a wider section of stakeholders with the help of tables, graphs, maps and diagrams, clearly highlighting the key findings of the detailed EIA report, viz.:
Essential project features, critical and unique environmental features of the site and the study area
- Alternatives considered15
- Terms of reference
- Key environmental issues and how each of these issues are proposed to be resolved,10 and how compliance to the applicable regulations is proposed to be achieved
- Controversial issues and outcome of the public consultation18
- Environmental impact statement in a clear and condensed form containing:
- The existing scenario of various components of the environment in the study area
- Significant environmental impacts assessed, corresponding mitigation measures suggested, and management of residual impacts
- Gist of the findings of additional/ special studies, if any
- Environmental management program including environmental management mechanism, environmental monitoring program for different life cycle phases of the project, compliance management, environmental enhancement, audit and management review
- Overall conclusion- impact on environment, residual impacts after mitigation measures, loss of natural resources, long term enhancement of natural resources, etc.
Evaluation of Executive Summary- Case studyMethodology
The EIA reports of all the 225 green-field projects (new projects proposed at new locations, generally un-developed/ under-developed), which were granted environment clearance19 in India in the period October 2016 to March 2018 were segregated sector-wise, viz. airport, cement, chemical, highway, industrial area, metallurgical, mining, oil and gas, petroleum pipeline, port, sugar and distillery, thermal power, and waste management projects. 15% of the EIA reports were then selected randomly from these sectors for evaluation while ensuring that the reports were prepared by different consultants.
The criteria for evaluation of an executive summary, proposed in table1consist of thecomponents, viz. introduction, key findings of EIA and action proposed, environmental management program, and general features.The evaluation of each criterion was done in the scale 0-3; 0 being non-inclusion of the criterion in the executive summary; 1 inadequate, 2 reasonably adequate and 3 adequate inclusion. The table also depicts distribution of 34 EIA reports of the green-field projects, prepared by as many consultants, against each criterion. The robustness of an executive summary is determined by aggregating the scores of each criterion and taking the mean, without assigning any weightages for the sake of simplicity. The degree of robustness is considered on the basis of the mean score- 3 being high, 2-3 satisfactory, 1-2 low, and <1 very low.
Table 1: Evaluation of Executive Summary in EIA Reports of Green-field Projects
|
SNo. |
Executive Summary Features |
Distribution of EIA Reports,% |
|||
|
Evaluation scale |
|||||
|
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Introduction |
|
|||
|
1 |
Background |
6.1 |
33.3 |
60.6 |
0 |
|
2 |
Site settings |
15.2 |
33.3 |
48.5 |
3.0 |
|
3 |
Environmental settings highlighting unique and critical environmental features of the site and study area |
3.0 |
3.0 |
93.9 |
0 |
|
4 |
Project proposal highlighting resource requirement, and activities having potential environmental impacts in different lifecycle phases of the project |
0 |
27.3 |
72.7 |
0 |
|
5 |
Terms of reference |
78.8 |
21.2 |
0.0 |
0 |
|
|
Key findings of EIA and proposed action |
0 |
|||
|
6 |
Significant impacts on different environmental components |
3.0 |
9.1 |
87.9 |
0 |
|
7 |
Specific mitigation measures suggested for significant impacts |
3.0 |
9.1 |
87.9 |
0 |
|
8 |
Residual impacts and their management |
100 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
9 |
Alternatives considered |
89.3 |
7.1 |
3.6 |
0 |
|
10 |
Outcome of public consultation, and controversies |
67.9 |
10.7 |
7.1 |
14.3 |
|
|
Environmental management program |
|
|||
|
11 |
Environmental management mechanism with budget |
33.3 |
51.5 |
15.2 |
0 |
|
12 |
Additional studies |
36.4 |
45.5 |
15.2 |
3.0 |
|
13 |
Environmental monitoring and compliance management |
18.2 |
57.6 |
24.2 |
0 |
|
14 |
Environmental enhancement measures |
84.8 |
12.1 |
3.0 |
0 |
|
15 |
EMPg audit and management review |
97.0 |
3.0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
General features |
|
|||
|
16 |
Overall conclusion |
45.5 |
6.1 |
45.5 |
3.0 |
|
17 |
Use of base maps, tables, diagrams, etc. for presentation |
18.2 |
33.3 |
45.5 |
3.0 |
|
18 |
Clear and consistent presentation of the critical facts that make up each environmental issue and resolution of the issues |
0 |
81.8 |
18.2 |
0 |
|
19 |
Concise discussion on key findings of EIA study |
0 |
100 |
0 |
0 |
|
20 |
Simple, non-technical language used without jargon |
0 |
6.1 |
93.9 |
0 |
|
21 |
Stand-alone document |
0 |
3.0 |
30.3 |
66.7 |
Findings and Discussion
It is observed from the evaluation that executive summary included as part of an EIA report is more of a ‘summary’ rather than ‘executive summary’ since it summarizes the report without bringing out the key findings11 of the EIA study. The critical facts10 that make up each environmental issue and their resolution, and brief discussion on key findings of the EIA study are not highlighted to facilitate decision making. Executive summaries in general dwell more on description of environment, and environmental impacts and impact mitigation and little on a) administrative mechanism and budget forthe environmental management program, environmental monitoring and compliance management,18 audit and management review; b) environmental enhancement measures; c) additional studies; and d) areas of controversy.20 Further, most of the executive summaries do not mention about the residual impacts after mitigation and their management, alternatives considered, terms of reference, and outcome of public consultation.11 The date of holding the public hearing meeting, however, finds a mention in some reports.Simple language is used in most of the executive summaries without jargon.13 The environmental settings and resource requirements for the proposed project are generally included. Half of the executive summaries described site settings, background and overall conclusion,15 and used tables10 for presentation, and two-thirds are found to be stand-alone.
The EIA process9 in India prescribes the structure of EIA reportswhereby ‘Executive summary’ is required to be included in an EIA report in addition to the chapter ‘Summary and Conclusion’.21% of the EIA reports evaluated did not contain executive summary though 86% of these included ‘Summary and Conclusion’ chapter like all the other EIA reports. The executive summaries in EIA reports are described in 5-42 pages; the mean, median and mode number of pages being 13, 11 and 15 respectively. The variations in the size of the executive summary in EIA reports may be observed from fig. 1. 55% of the executive summaries, described in more than ten pages did not meet the requirements of EIA regulation.9 24% of the executive summaries were short and described in seven or less pages.11
The range of scores of evaluation may be observed from fig. 2; the mean, median and mode scores being 1.12, 1.14 and 1.14 respectively. The evaluation reveals that 18% of the executive summaries had very low degree of robustness and the remaining 82% had low degree of robustness. These findings could not be validated as no similar studies on executive summary are found in the literature.Nevertheless, the findings of the present study are in agreement with that reported21 inclusion of ‘no or poor’ executive summary in EIAs as one of the common problems with EIAs. The evaluation score of EIA reports was reported15 to be in the range 4.1-5.2 on the scale of 10. The low score of executive summaries in the present study confirms that effectiveness and quality of an executive summary could only be as good as that of a clear and comprehensive EIA report based on rigorous studies, sound data and consistent analysis and interpretation.11 Further, most of the executive summaries do not give perspective22 of the report and equip the reader with a summary of objective, methodology, and findingsof the report.
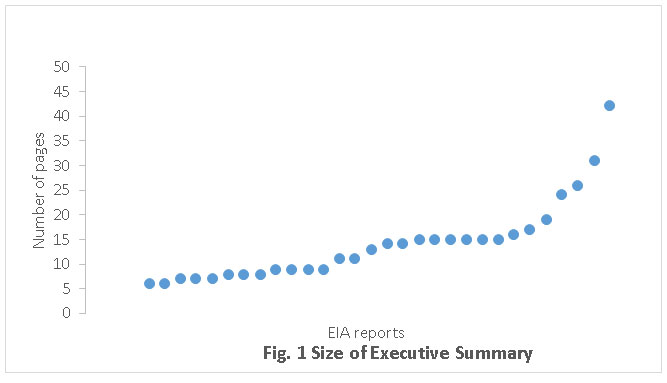 |
Figure 1: Size of Executive Summary Click here to view figure |
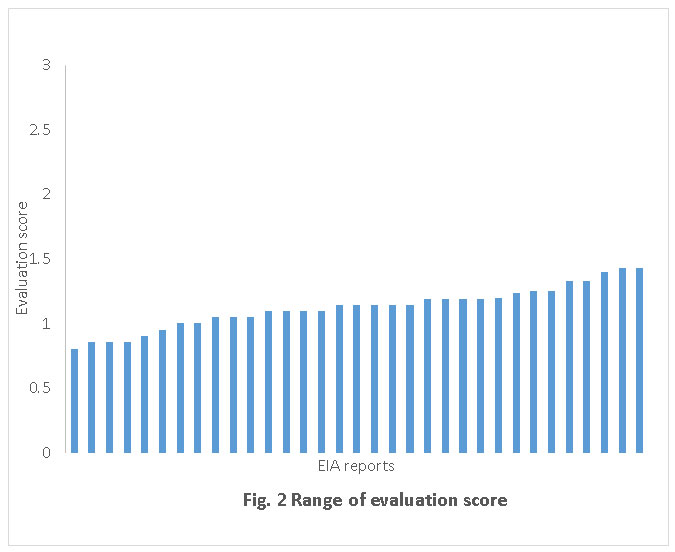 |
Figure 2: Range of Evaluation Score Click here to view figure |
Conclusion
Executive summary is an extremely important part of an EIA report since only this part of the EIA report is often read by most of the stakeholders including decision makers. Executive summaries of 34 EIA reports of different project sectors, prepared by different EIA consultantsand granted environmental approvals, were evaluated for their robustness. It is found that the degree of robustness of executive summaries is low. Further, the term ‘executive’ in executive summary is not justified since lengthy summaries of EIA reports are presented without highlighting key findings of the EIA studies. Even though the executive summaries are long, these are incomplete and several aspects consideredimportant for aiding decision making are not covered. Executive summary of an EIA report achieves a great importance especially in the large developing economies where a large number of development projects are proposed and the competent authority is under severe pressure of time for taking decision on the proposals in a time bound manner.However, no effortseems to have gone into improving executive summary part of an EIA report as this aspect has not received attention of researchers, professionals, reviewers and decision makers.
Guidelines are proposed to facilitate the EIA professionals in the preparation of a robust executive summary,which is comprehensive, effective and objective in aiding decision making on grant of the environmental approval to the proposed development projects. Executive summary part of an EIA report needs to summarize and highlight truly the a) key aspects of the settings of the site, b) project description and project-related activities over project lifecycle which have a potential of causing environmental impacts, c) baseline environmental settings including unique and special features, d) significant impacts determined along with the suggested mitigation measures, e) residual impacts after mitigation measures, f) environmental management program,g) loss of natural resources, h) controversial issues, if any, and i) outcome of public consultation. Considering that an executive summary should be able to serve as a stand-alone document for distribution to the stakeholders, it should not contain reference to any of the contents in the body of the EIA report, and should be prepared in a manner that it is easily understood by those who do not possess expertize in preparing EIA studies, with a special focus on the non-technical stakeholders at large. It needs to be duly translated in the regional language, if required so that a larger population is able to read it and participate in public consultation.
References
- Business Dictionary.Definition of executive summary .http://www.business dictionary.com/definition/executive-summary.html. 1997.(Accessed 15June 2018).
- Wikipedia. (2001). Executive summary .https://en. wikipedia.org/wiki/ executive_summary. 2001. (Accessed 15 June 2018).
- Glasgow Caledonian University. Executive summary and conclusion .https ://www.gcu.ac.uk/library/smile/writingandnumeracy/executivesummaryandconclusion/.1993. (Accessed 17 June2018).
- Bonjour P.How to write an executive summary. https://www.inc.com/guides /2010/09/how-to-write-an-executive-summary.html. 2010 (Accessed 15 June 2018).
- World Bank.Environmental assessment sourcebook.Washington, D.C. :Environment Department, WB, 1999.
- MTR Corporation. Environmental impact assessment of express rail link .https://www.epd.gov.hk/eia/register/report/eiareport/eia_1692009/ES/pdf/ES_TOC%20 (eng).pdf. 2009. (Accessed 17 June 2018).
- Department of Environmental Affairs and Tourism. Environmental impact reporting. Integrated environmental management information series 15.Pretoria: DEAT, 2004.
- Commonwealth of Australia. Environmental management plan guidelines. Canberra: Department of Environment, COA, 2014.
- Ministry of Environment and Forests.Environmental impact assessment notification.New Delhi: MOEF, 2006.
- Lohani B, EvansJ.W, Ludwig H, Everitt R.R, Carpenter R.A,Tu S.L.Environmental impact assessment for developing countries in Asia- overview. Manila: Office of the Environment, Asian Development Bank, 1997.
- Sadler B, McCabe M.Environmental impact assessment training resource manual.Geneva: Division of Technology, Industry and Economics, UNEP, 2002.
- Wood C.Environmental impact assessment: a comparative review. Harlow: Longman Group Ltd., 1995.
- European Union.Directive 2014/52/EU. European Parliament and the Council, Amendment of the Directive 2011/92/EU. Brussel: EU, 2014.
- World Business Council for Sustainable Development. Environmental and social impact assessment (ESIA) guidelines. Geneva: WBCSD, 2005.
- Rathi A.K. A. Evaluation of project-level environmental impact assessment and SWOT analysis of EIA process in India. Environmental Impact Assessment Review.2017; 67 31-39.
CrossRef - World Business Council for Sustainable Development.Guidelines for Environmental and Social Impact Assessment. Geneva: WBCSD, 2016.
- Panigrahi J.K,Amirapu S. An assessment of EIA system in India. Environmental Impact Assessment Review.2012; 35 23-36.
CrossRef - Rathi A. K. A.Environmental impact assessment: a practical guide for professional practice. Ahmedabad: Akar Unlimited, 2016.
- Ministry of Environment and Forests. Online submission & monitoring of environmental clearances. http://environmentclearance.nic.in/onlinesearch.aspx?pid=ecg. 2014. (Accessed 20 June 2018).
- California Government.Environmental impact report.http://www.dot. ca.gov /ser/vol1/sec5/ch36eir/chap36.htm. 2018.(Accessed 31 August 2018).
- Floroiu R.Environmental (and social) impact assessment instruments.Paper presented in World Bank Safeguard Workshop Training held in May/ June 2012.https://slideplayer.com/slide/8055387/.2012. (Accessed 15 March 2018).
- Smith K.How to write executive summary.https://blog.pandadoc.com/how-to-write-executive-summary/.2017. (Accessed 31 August 2018).







