Water quality assessment of Newaj river at Rajgarh, Madhya Pradesh, India
Naveen Malviya1 * , Suman Malik1 and Avinash Bajpai2
1
Makhanlal University,
Bhopal,
India
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CWE.4.2.27
Newaj river is the ‘Life Line’ for the city of Rajgarh as it is the major source of water supply for the entire city. The study represents the results of physico-chemical parameters such as pH, Dissolved Oxygen, Biological Oxygen Demand and Chemical Oxygen Demand during different seasons from Nov. 2008 to Oct. 2009. It was observed that BOD and COD increased regularly but DO decreased in summer season except reference water sampling station. BOD, COD, DO values have deviated from the standard values. These values show that river water can directly be used for irrigation and for drinking purpose, it needs treatment.
Copy the following to cite this article:
Malviya N, Malik S, Bajpai A. Water quality assessment of Newaj river at Rajgarh, Madhya Pradesh, India. Curr World Environ 2009;4(2):425-427 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CWE.4.2.27
Copy the following to cite this URL:
Malviya N, Malik S, Bajpai A. Water quality assessment of Newaj river at Rajgarh, Madhya Pradesh, India. Curr World Environ 2009;4(2):425-427. Available from: http://www.cwejournal.org/?p=1008
Download article (pdf)
Citation Manager
Publish History
Select type of program for download
| Endnote EndNote format (Mac & Win) | |
| Reference Manager Ris format (Win only) | |
| Procite Ris format (Win only) | |
| Medlars Format | |
| RefWorks Format RefWorks format (Mac & Win) | |
| BibTex Format BibTex format (Mac & Win) |
Article Publishing History
| Received: | 2009-08-24 |
|---|---|
| Accepted: | 2009-09-23 |
Introduction
The Newaj river is the left bank tributary of the river Parwan which is a right bank principal tributary of Kalisindh River. In the present years due to the growth in population, urbanization, settlement of brick manufacturing plant, deforestation etc. the river is contaminated regularly and the maintenance of the quality of river water will be a severe problem in the years to come. The present study aims to assess the Newaj river water quality at different sampling stations with most critical parameters, i.e. pH, DO, BOD, COD. The physico-chemical parameters of the river water have been studied by many co-workers like Chakrabarthy et al1 and Rai2
Materials and Methods
For regular monitoring of the chemical characteristics of Newaj river, the following sampling stations selected were (SS-1) nearby gra m Kishangarh, (SS-2) brick manufacturing plant on bada pull, (SS-3) located near agriculture land of Madapura (SS-4) reference water sampling station, (SS-5) near forest area and (SS-6) the idol emersion ghat. Water samples were collected on a monthly basis from all six sampling stations. All the chemicals used were of analytical grade and the reagents were prepared in distilled water. The pH is measured by Systronic pH-meter 361. The dissolved oxygen is determined by Winkeler's method [APHA 1989]3 with azide modification, BOD is determined by BOD incubation method and COD by potassium dichromate open reflux condenser method.
Results and Discussion
The pH value of the water was slightly alkaline (7.4-8.5) and only minor fluctuation in pH was recorded. The study shows that the Dissolved Oxygen range over a period of one year was found to be maximum at (SS-4) when compared to other stations. Dissolved Oxygen was found to be low specially in summer season. A similar observation has been made by Charu et al4. Except (SS4), on other stations the low value of DO is due to the pollution like organic matter, run off agriculture land and low solubility of gases.
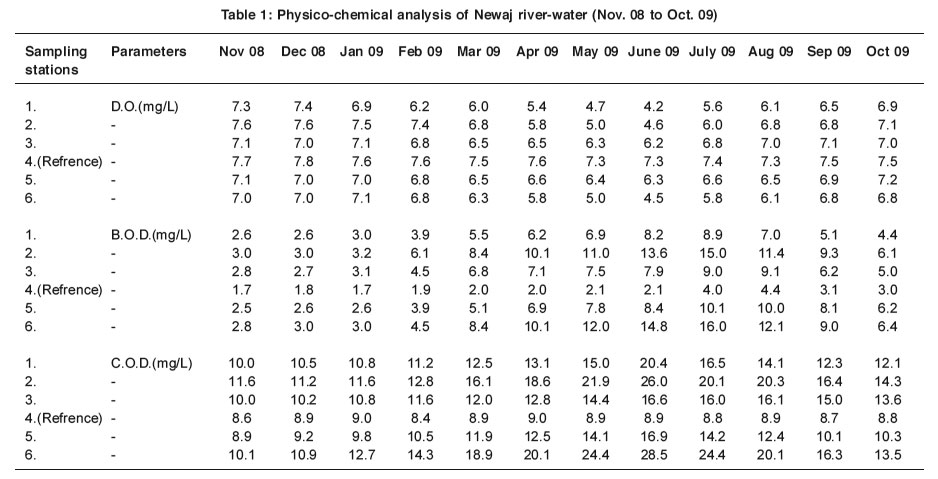 |
Table 1: Physico-chemical analysis of Newaj river-water (Nov. 08 to Oct. 09) ​Click here to view table |
​​​​​​
BOD range in summer season at (SS-2) and (SS-6) was found to be high. This is mainly due to some open drains of waste water. Similarly COD values were found to be high in summer. This may be due to reduced water flow and organic matter in large amounts. Observations show that while the reference water sampling station has high DO and low BOD, COD values during the whole year, but at the other sampling stations the DO values are low while BOD and COD values are high which depict deteriorating water quality of Newaj river. Water quality along reference water sampling station is in permissible limits but at other stations it is not in permissible limits (ISI 1983)5
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Principal, Sadhu Vaswani College, for providing library and laboratory facilities as well as valuable suggestions during the experimental works.
References
- Chakrabarthy, R.D. Ray, P. and Singh, S.B.; A quantitative study of the plankton and the physico - chemical condition of the river Jamuna at Allahabad in 1954-55. Indian J. Fish.(1959) 6:(1) 186-203.
- Rai, H.; Limnological studies of the river Yamuna at Delhi India par t I Relation between the chemistry and the state of pollution in the river Yamuna Arch. Hydrobiol (1974 a) 73:(3) 369-393.
- APHA 1989, standards method for the examination of water and wastewater, 17th Edn. Washington DC APHA, AWWA, WPFC 2005.
- Charu, P. Savita, D. and Rajnish, S.; Seasonal Variations in physico-chemical characteristics in upper lake of Bhopal; Asian J. Exp. Sci.(2006) 20: (2).
- ISI, Indian standard : Specification for dr inking water New Delhi India, Indian standard institution (1983).
- WHO (Wor ld Health Organization). Guidelines for drinking water quality vol. I Health cr iter ia and other suppor ting information Geneva WHO (1984).
- Pulhar ya, J.P. Malviya, S.; Pollution of Narmada river at Hoshangabad in M.P. and suggested measure for control in R.K. Trivedi (Ed) : Ecology and Pollution of Indian rivers, New Delhi (1998).






